Is your equipment rusty? Are your pool liner and accessories discolourating? Is your pool liner wrinkled? Whatever the problem, the AZUR brand offers simple and effective solutions!
There are 4 possible causes of equipment degradation:
- Low pH;
- Total low alkalinity;
- Low calcium hardness;
- Chlorine level above 3 ppm.
In all 4 cases this means that the water is corrosive.
Here are the solutions for each of these problems.
Low pH (below 7)
A correct pH level is essential to maintain the balance of the pool water. A pH that is too low is a sign of excessive water acidity and can have serious consequences.
When the pH level is too low, the water is acidic. This acidic water can cause corrosion of the water heater, salt system, UV system, pump and filter. This will of course reduce the life span of your equipment.
In addition, a high acidity level of the water will cause the pool liner to wrinkle and make it look like the skin of an orange. The liner will also slowly discolour and lose its patterns.
To increase the pH to its ideal level of 7.5, simply use pH+. To know the exact amount to add, consult the dosage indicated on the container label or do a water test in store.
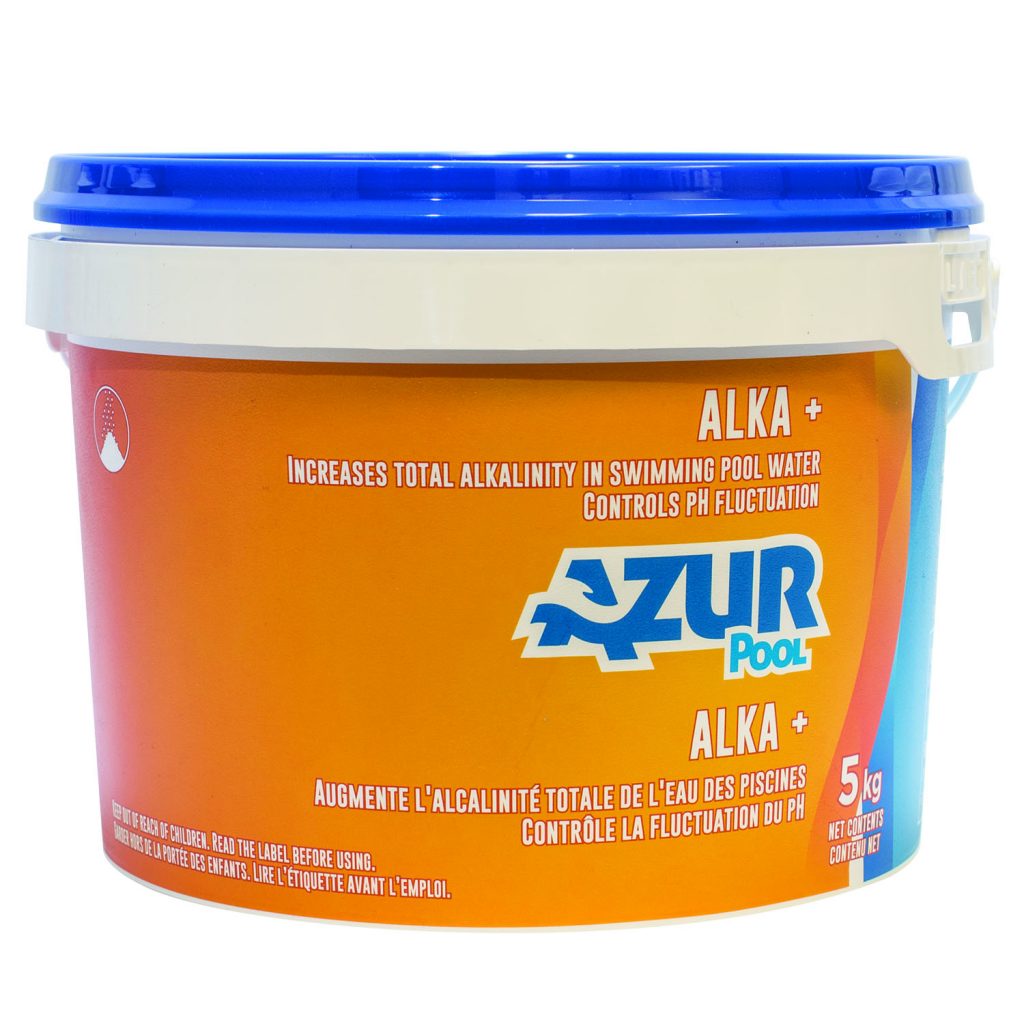
Low Total Alkalinity (below 80 ppm)
Damage caused by water with low Total Alkalinity will be the same as when the pH is low.
Once Alkalinity is well adjusted, it should no longer fluctuate much, unless:
– Heavy rains for several days;
– That a very acidic product (such as chlorine tablets) is regularly added to the pool.
To increase Total Alkalinity to its ideal level of 100 ppm, simply use ALKA+. An in-store water test will give you the exact amount to add.
Low calcium hardness (below 200 ppm)
The damage caused by water with a low calcium hardness will be the same as when the pH or total alkalinity is low. However, it will be even worse if the pool is made of concrete instead of being covered with a liner. If the Calcium Hardness is low, the concrete walls will disintegrate.
Once the Hardness is well adjusted, it should not fluctuate much.
To increase Calcium Hardness to its ideal level of 200 ppm, simply use CALCIUM+. An in-store water test will give you the exact amount to add.
Chlorine level (above 3 ppm)
A chlorine level above 3 ppm will make the water corrosive. It is important to maintain a chlorine level between 1 and 3 ppm at all times. If you see that the chlorine level is too high, simply stop adding chlorine until it drops to the appropriate values.
Owners of swimming pools with salt systems often encounter this problem. Most of the time, the dial of the device is adjusted too high and produces too much chlorine. Be sure to do a chlorine test every week, whether you use chlorine or a salt system.
Summary – to avoid damaging the pool
– Low pH: Adjust the pH between 7.2 and 7.8. Increase the pH with pH+.
– Low total alkalinity: Adjust the total alkalinity between 80 and 120 ppm. Increase alkalinity with ALKA+.
– Low calcium hardness: Adjust the calcium hardness between 200 and 300 ppm. Increase the calcium hardness with CALCIUM+.
– Sanitation level (chlorine) above 3 ppm: Adjust the sanitation level between 1 and 3 ppm.